1. Install Server Backup Manager using YUM
1.1 Configure the YUM Repository
YUM is the easiest way to keep programs up-to-date on RedHat-compatible distributions. YUM downloads and installs the latest version of a program. You should configure the YUM repository to manage installations of and upgrades to Server Backup Manager.
First, create a YUM .repo file with the R1Soft repository information. Save the file in the yum.repos.d directory, which is typically located in /etc/.
1. Open the new file with a text editor such as vi or nano:
or

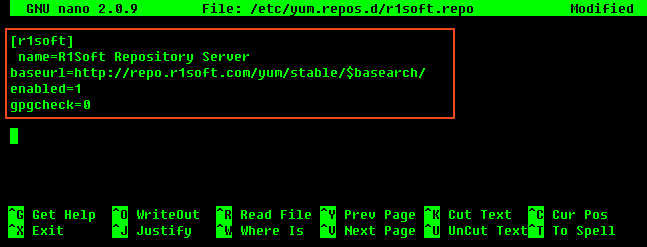
2. Insert the following text into the file and save the file:
| Tip $basearch is a Yum variable, i.e., the base architecture (32-bit, 64-bit, etc.). |
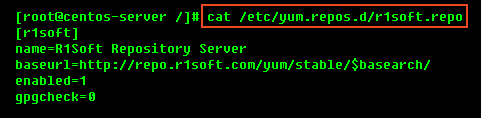
3. To verify what is written to the file, use the following command:
1.2 Install the package
1. With the installed YUM repository, you can use the following command to install Server Backup Manager:
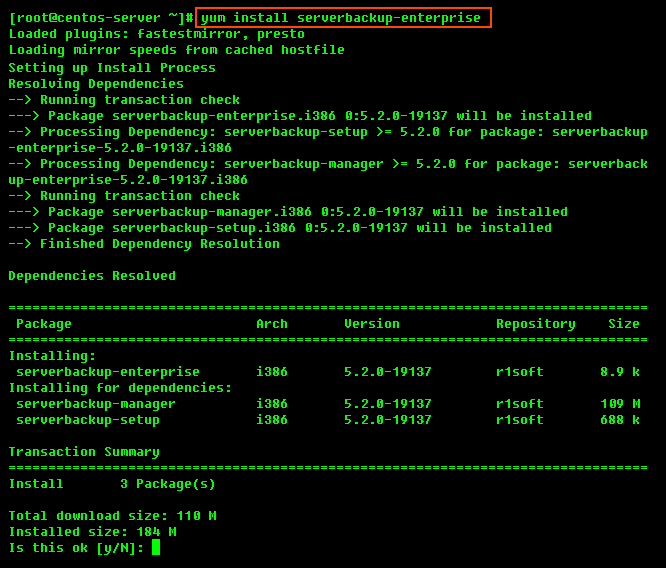
2. Then, enter "y" to install all the dependencies of the package.
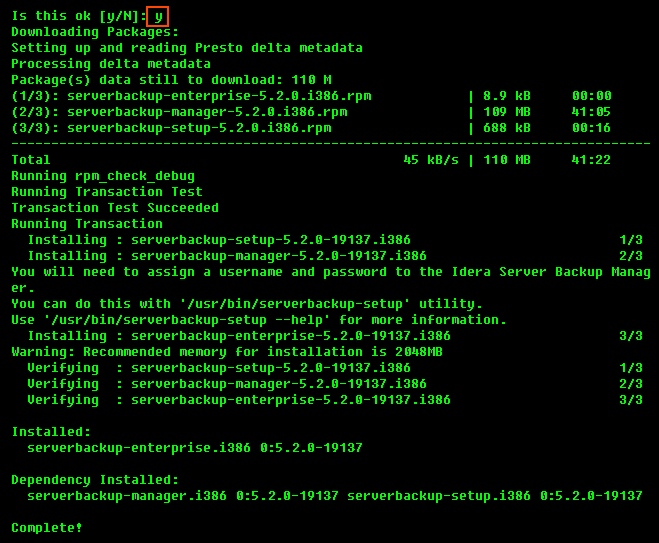
3. Once complete, you can use the help command to list all available options:
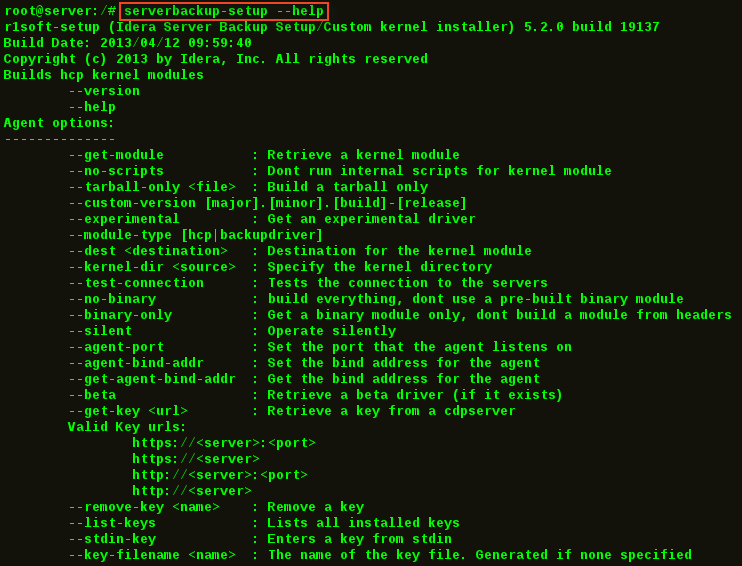
4. Now, proceed to the Step 3.
2. Install the Server Backup Manager manually using rpm
2.1 Download Server Backup Manager
See Obtain Linux Backup Manager.
2.2 Make sure you can unzip the download
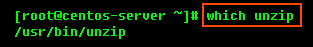
Most Linux distributions come with the unzip utility pre-installed. To determine if you have the unzip utility, run:
This should return an output similar to the following:
If it returns the following output, you need to install the unzip utility first:
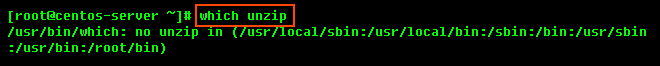
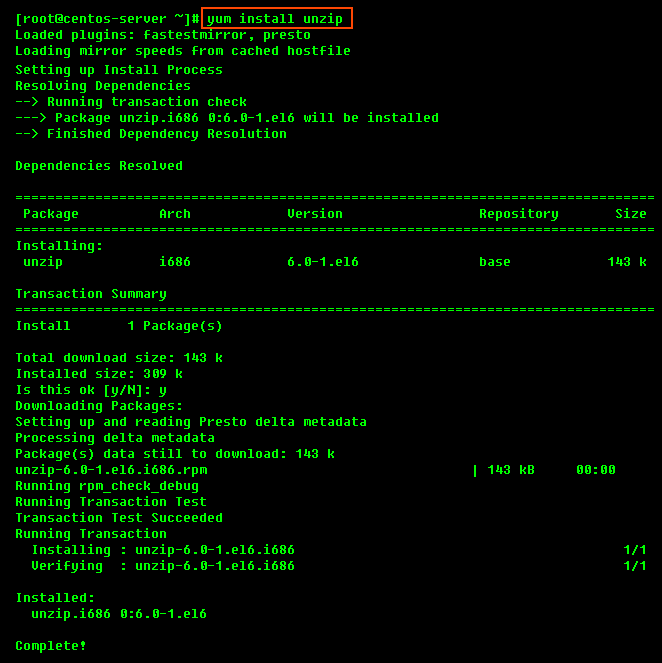
To install unzip on RHE, CentOS, and Fedora:
2.3 Extract the ZIP file
We recommend creating a temporary directory to which you can extract the contents of the ZIP file.
1. Use the mkdir command to create a temporary directory (in our case, serverbackup).
2. Use the mv command to move the archive to that directory. Note that Linux file names are case-sensitive. Make sure you type the name correctly (in our case, "ServerBackup-Enterprise-linux32.zip").
3. Use the cd command to go to that directory.
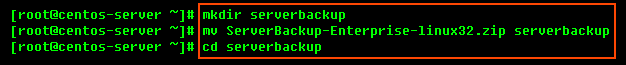
4. Use the unzip command to extract the files.
!unzip-ent_5.2.0.png!Run:

2.4 Install the packages
| Notice You must be a Linux root user to install the Server Backup Manager. |
The archive you have extracted contains two folders: one with .deb packages (in our case, "enterprise-manager-deb") and one with .rpm packages ("enterprise-manager-rpm"). If you are installing on RedHat and CentOS, select the .rpm package.
Each folder contains a set of Server Backup components:
- serverbackup-setup
- serverbackup-manager
- serverbackup-enterprise
You will need to install all of them in one step. Use the cd command to go to the folder with the packages (in our case, deb-linux32)
And run the following command:
RPM 32-bit (x86) / RPM 64-bit (x86_64)
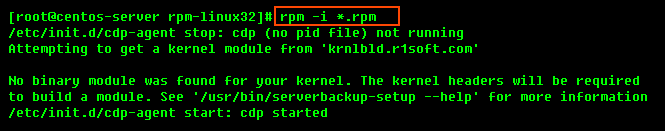
| Note The installed files are located in the /usr/sbin/r1soft directory. The Manager startup script is /etc/init.d/cdp-server. |
| Note You do not need to install the kernel module on the Server. |
3. Configure and start the Server Backup Manager Web-based user interface
1. You must define a username and password for Backup Manager Web Interface before you can begin using Server Backup Manager.
After running this command, you will see an output similar to the following:
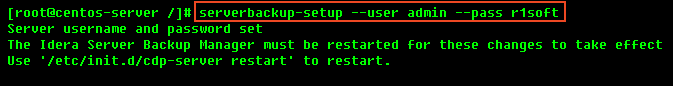
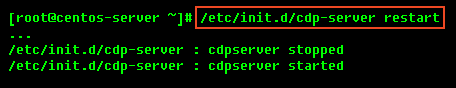
To restart the Server Backup Manager run the following command:
2. Configure Ports if necessary.
By default, the embedded web server in Server Backup Manager required for the Web-based Interface will listen on TCP ports 80 (HTTP) and 443 (HTTPS). These ports are frequently used by your Linux server (e.g., by Apache). If you are already using ports 80 and 443, you will need to define different ports. Ports 8080 (HTTP) and 8443 (HTTPS) are recommended alternatives to standard 80 and 443. However, you can choose any other valid and unused TCP port.
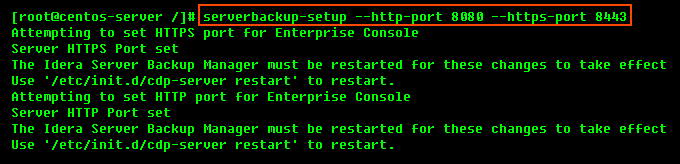
| Note You may need to change the firewall rules, depending on where you are connecting to the Web Interface from. |
See also: Configure Server Backup Manager on Linux.
3. Start the Web Interface (Backup Manager):

You should now be able to connect to the Server Backup Manager Web interface using Firefox or Internet Explorer. See Access Server Backup Manager Web interface.
